Search engines rely on sitemaps to enhance their understanding of websites’ structures and content. A sitemap serves as a blueprint, listing all pages, videos, and other content types, enabling search engine crawlers to navigate and index them effectively. But how do search engines use sitemaps?
We will explore the intricate relationship between search engines and sitemaps, shedding light on a process that shapes our online experiences.
Whether you’re a website owner, a digital marketer, or simply curious about the inner workings of the web, we will offer valuable insights into the unseen mechanisms powering internet search.
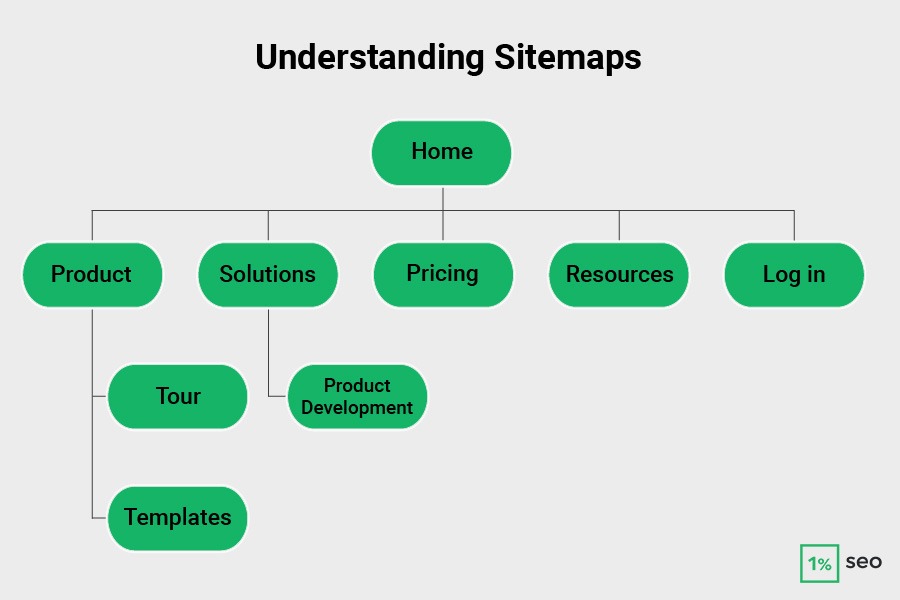
Understanding Sitemaps
A sitemap is a file that lists all pages on a website, helping search engines understand and navigate the site’s structure. It shows important pages and recent changes and can use XML or simpler formats. There are different types of sitemaps: XML sitemaps for search engines, HTML sitemaps for users, and specialized ones for images and videos.
These tools make it easier for search engines to find and index all content, including details about multimedia elements. Using sitemaps lets you ensure your content is more easily discovered and properly categorized by search engines.
Are sitemaps still relevant?
Sitemaps may be valuable tools in modern web design. They guide search engines efficiently through your site’s structure, ensuring no pages are overlooked. Sitemaps provide a clear roadmap, enabling search engines to discover and index your content more quickly and comprehensively.
Sitemaps are especially helpful when you add new content to your site. Updating your sitemap allows search engines to find your new pages promptly, which means your new content can appear in search results faster.
Moreover, some websites have pages that are challenging to find through normal links. A sitemap ensures search engines can still locate these pages. This functionality is particularly crucial for large websites or those with complex structures.
Highlighting important content
Sitemaps let you tell search engines which pages matter most. You can give each page a priority score. This helps search engines know which pages to focus on first. You can also use sitemaps to say how often your pages change.
If a page changes daily, you can tell search engines to check it often. If it rarely changes, they don’t need to check as much. Special sitemaps can help websites with lots of images or videos. These sitemaps give extra details about your media, which help your images and videos appear more in search results.
How Do Search Engines Use Sitemaps?
Discovering new content
Search engines rely on sitemaps to find new content quickly and easily. When you add a new page to your website, you include it in your sitemap. Search engines regularly check these sitemaps. This way, they can discover your new content much faster than if they had to crawl your entire site.
Sitemaps also help search engines find all your content, even pages that might be hard to reach through normal navigation. This is especially useful for large websites or those with complex structures. Listing all pages in the sitemap ensures that search engines don’t miss any important content.
Using sitemaps also makes the crawling process more efficient. Instead of guessing where to look, search engines have a clear roadmap of your site. This saves time and resources for both the search engine and your website.
Understanding website structure
You can use sitemaps to show search engines how your website is organized. They illustrate the connections between pages and sections, helping search engines navigate your site efficiently and grasp its overall layout.
Furthermore, sitemaps help search engines understand your content’s themes and categories. By grouping similar content in your sitemap, you provide clues about your information’s organization, which enhances their understanding of your site’s focus.
Search engines compare your sitemap with your site’s link structure to verify information. This comparison helps them understand how visitors might navigate your site and identify which pages you prioritize.
Prioritizing content
Sitemaps allow you to signal which pages are most important on your site. You can assign priority levels to different pages in your sitemap. Search engines use this information to guide their crawling and indexing efforts. They may give more attention to pages you’ve marked as high priority.
Additionally, you can use sitemaps to tell search engines how often your pages are updated. This information helps search engines decide how frequently to recheck your pages. Pages that change often may be crawled more frequently, while static pages might be checked less often.
Search engines use this update frequency information to assess the freshness of your content. They compare it with actual changes they observe on your site. This insight helps search engines identify your site’s most active parts, potentially impacting your pages’ ranking in search results.
How to Create a Sitemap?
Creating a sitemap involves structuring an XML file that helps search engines like Google and Bing better understand and index your website. For small sites, you can manually create an XML file using basic text editors, starting with an XML declaration and specifying each page URL within <url> tags.
Larger sites benefit from automated tools such as plugins or online generators. These tools automatically simplify the process by crawling your site and generating a comprehensive sitemap.
Once your sitemap is ready, it is essential to submit it to search engines via their respective webmaster tools (like Google Search Console or Bing Webmaster Tools). This involves logging into the tools, entering your sitemap’s URL, and submitting it for indexing.
Regularly updating your sitemap and monitoring its performance ensures that search engines accurately reflect changes to your website. This enhances its visibility in search results.
Best Practices for Sitemaps
To maintain an effective sitemap:
- Keep it updated with changes to your website—whether daily, weekly, or monthly.
- Regularly remove outdated URLs and fix errors to ensure accuracy.
- Organize your sitemap by grouping similar content and including essential information for each entry.
For larger websites, consider using multiple sitemaps alongside an index file. Prioritize important pages appropriately, avoiding excessive use of high-priority tags. You should monitor how search engines utilize your sitemap and adjust based on data-driven insights.
Conclusion
Sitemaps are crucial for helping search engines efficiently navigate and understand websites. They provide a structured roadmap of your site’s content, which speeds up indexing, enhances content discovery, and prioritizes your pages.
They’re especially valuable for large or complex websites, ensuring all-important content is found during crawling. However, creating and maintaining an effective sitemap takes effort.
The potential benefits for your site’s visibility and search engine performance make this effort worthwhile. Understanding how do search engines use sitemaps allows you to follow best practices and enhance your SEO efforts.
Remember to update your sitemap regularly, organize content logically, and submit it to search engines. Sitemaps remain essential for web admins and SEO professionals looking to optimize their online presence and improve search rankings.