Keyword research is a fundamental aspect of digital marketing that can significantly boost your visibility and engagement. In this article, we dive into the essential techniques and tools that will empower you to uncover the right keywords for your content strategy.
Keyword research forms the bedrock of successful SEO (Search Engine Optimization) and content creation. By identifying the terms and phrases your audience uses, you can tailor your content to meet their needs and capture their interest.
This process goes beyond mere guesswork—it involves strategic thinking and data-driven insights. But how to do keyword research for best results?
We’ll explore step-by-step methods to find keywords that resonate with your target audience and align with your business goals. From selecting the right tools to analyzing competition and search trends, mastering this process can elevate your digital presence.

What Is Keyword Research in SEO?
Keyword research involves finding popular words and phrases (keywords) that people type into search engines. This helps optimize your website and content to rank highly in search engines. Keyword research involves researching your industry, products, competitors, and customers.
The goal is to identify relevant keywords with high search volumes and moderate competition. You then optimize website pages, create content like blog posts and videos, and earn backlinks from other sites. All while using those target keywords in a natural way that matches the search intent.
Proper keyword research is crucial for driving targeted organic traffic through SEO and digital marketing. Without it, you’ll be missing out on valuable search visibility and website visitors. A thorough keyword research process is fundamental for any successful SEO strategy. Now, how to do keyword research for SEO?
Preparing for Keyword Research
Identifying Your Niche and Audience
The first step in preparing for keyword research is clearly identifying your specific niche or industry. What products or services do you offer? What topics do you cover? Clearly define this upfront. Next, research your ideal target audience. Look at demographics like age, location, interests, and pain points.
Understanding who you are trying to reach is crucial as it not only helps you analyze what their search intent is but it helps analyze how your competitors operate in the same niche. See what keywords they are targeting and look for potential gaps you can fill. Knowing your niche allows you to uncover relevant keywords.
Setting Goals
Before diving into keyword research, set clear goals for what you want to achieve. Are you looking to rank high on blog posts, or is your site e-commerce-focused? Then, search for keywords accordingly.
Alternatively, you may want to reach certain geographic locations or demographic groups. If so, you’ll need to find localized and niche-specific keywords accordingly. Another potential goal is boosting sales conversions from your website traffic. For this, find intent-driven keywords that indicate high purchase intent or transaction likelihood.
How to Do Keyword Research
Seed Keyword Base
To start your keyword research, you first need to generate an initial list of relevant seed keywords related to your niche. Seed keywords are, in fact, the starting point of keyword research. They help identify your niche and competitors. Brainstorm words and phrases that your target audience would likely use when searching for your products, services, or content topics online.
For example, if you sell baby clothes, then your seed keywords could be baby, clothes, cotton, baby sets, etc. As the name suggests, these are just keywords to get your ideas and mind on the right track. It doesn’t necessarily mean they’ll help with targeting pages on your website.
Coming up with seed keywords shouldn’t take long. Just think of the first words that pop into your head, and note them down. Once you have 10-20 seed keywords jotted down, you are ready for the next step.
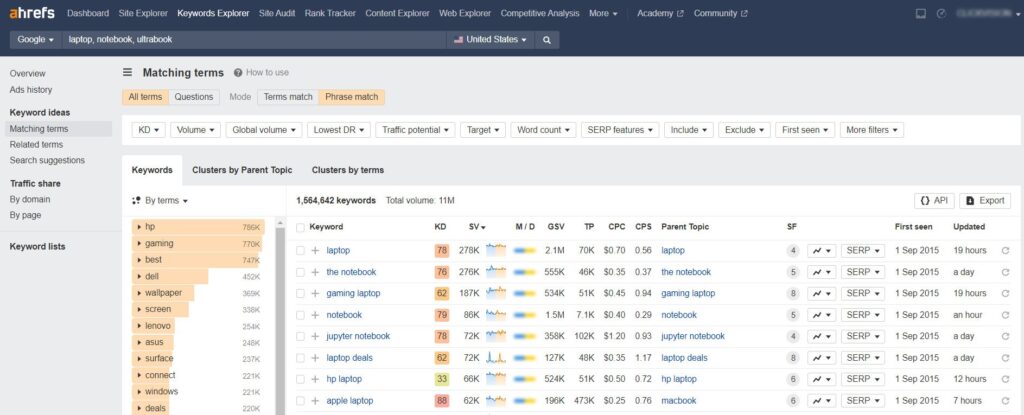
Analyzing Competitors
It’s a good strategy to look for keywords your competitors rank for that you don’t have any content optimized around yet. But first, you need to see who your competitors are. Search on Google one of the many seed keywords and see who ranks on the first page.
A side note: If none of the seed keywords lead to a search that resembles your site, then you are doing something wrong. Try being more specific in your search.
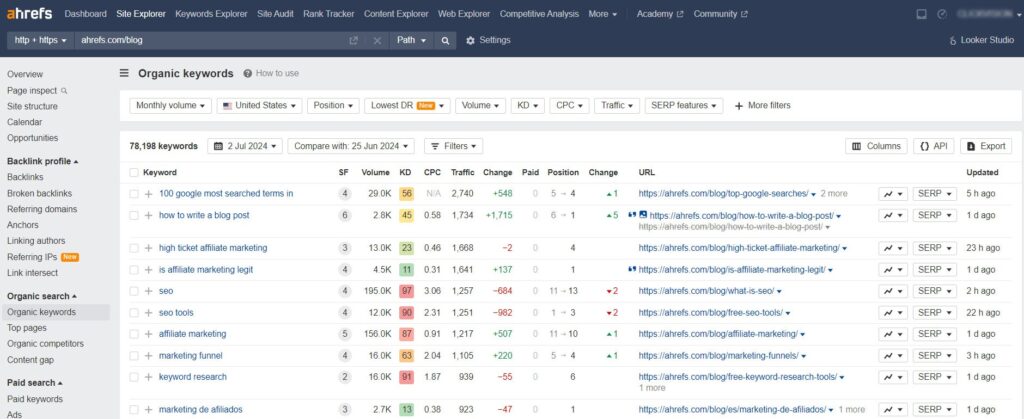
Once you’ve found a competitor, turn to competitive intelligence tools like Ahrefs, SpyFu, and SEMrush to dive deep into your competitors’ full keyword portfolios and top content. After you go from competitor to competitor, you’ll have a set list of relevant keywords. The various keyword tools allow you to enter your competitors’ website URLs. They will analyze and break down all of the top keywords that each competitor website ranks for in search results.
Finding plenty of keywords represents an opportunity to create better content on the already-written topics or create brand-new content and get higher rankings on search engines. Prioritize keywords that have high search volumes but aren’t extremely competitive yet. Don’t just go with your initial guesses – let the data inform your seed keywords. The more comprehensive this initial base is, the better your final keyword list will be.
Keyword Research Tools
Free Keyword Tools
While the paid tools are very powerful, Google’s free options can still be quite useful for basic keyword research on a budget. The Google Keyword Planner is free to use and allows you to find keywords for SEO purposes, search volumes while searching on Google itself, and scrolling to the bottom provides related searches.
Don’t just rely on a single tool – using multiple tools is recommended for well-rounded keyword research.
Paid Keyword Tools
There are quite a few popular keyword research tools out there to use beyond just Google’s free tools. A few of the most widely used are Ahrefs, SEMrush, Moz’s Keyword Explorer, and Keyword.io. These paid tools make it easy to use.
Just enter a seed keyword, and the tool will provide you with tons of related keyword suggestions. It also gives valuable metrics like search volumes, competition levels, and keyword difficulty scores. Many tools also offer advanced features like SERP analysis, keyword grouping into topic clusters, and content gap analysis.
Expanding the Keyword List
Once you have a solid base of keyword data from research tools and competitor analysis, you can explore additional methods to expand your final keyword list. Try modifying your keywords by adding related modifiers like locations, product names, industry jargon, and other relevant word variations.
You can also look at the related search suggestions at the bottom of Google’s search results pages for even more ideas. Participate in industry forums to understand your audience’s language. Apply audience research, use cases, searcher intent, and common questions in your niche to ideate new keyword angles.
Add modifiers for things like skill levels (beginner, advanced), frequent misspellings, comparisons, and product specifications. Review your website search queries and FAQs for more potential keywords to target. The options are endless – get creative to uncover untapped keyword opportunities!
How to Evaluate and Select Keywords
Keyword Metrics
When evaluating keywords, there are several key metrics to consider. Search volume shows how many times on average that keyword is searched per month – higher volumes typically mean more potential traffic.
Keyword difficulty scores estimate how difficult it will be to rank for that keyword based on the competition level. For keywords you may want to bid on for paid ads, consider the cost-per-click (CPC) metric. This indicates how much it would cost you to rank for that keyword term.
Look at metrics like clickthrough rate (CTR), which estimates how likely people are to click a result for that keyword. Track your keywords’ current rankings as well and use these metrics together to get a full picture of a keyword’s value and competitiveness.
Prioritizing Keywords
With your keyword research data and metrics in hand, you’ll want to prioritize which keywords to target first. A good approach is to focus initially on keywords that are highly relevant and centered around your core products, services, and brand.
Look for higher search volume terms but with lower-moderate competition levels to start. You can also prioritize keywords with the highest potential return on investment in terms of estimated traffic and conversion potential.
Prioritize keywords that align with your current marketing objectives – whether that’s boosting brand awareness, driving leads, or increasing sales. Consider prioritizing buyer keywords over informational keywords initially. Also, leave room to periodically reevaluate your keyword priorities as your business needs evolve.
Grouping Keywords
Once prioritized, organize and group your keywords into logical clusters. One method is to group keywords into topic clusters or themes so you can create tightly focused content pieces targeting those keyword groups.
You can categorize keywords based on the dominant user search intent behind them. These intents include informational, navigational, commercial, or transactional purposes. Another approach is mapping keywords to the different stages of the buying cycle or customer journey.
Use a spreadsheet or keyword grouping tool to organize your lists. Establish a clear naming convention. And leave room for new keyword groups as you continue to expand your research. Having an organized, systematic process helps maximize your keyword targeting.
How to Do Keyword Research for SEO
Creating Optimized Content
High-Quality content optimization
When doing keyword research for SEO, the primary goal is creating high-quality, keyword-optimized content that ranks well and drives targeted search traffic. Start by developing content that thoroughly covers the topic and answers your audience’s needs.
Then, strategically incorporate your target keywords throughout the content in a natural and readable way. Place them in titles, headers, body copy, URLs, meta descriptions, and image alt text as needed. Stuffing keywords is a spam tactic to avoid, and the content should provide a great user experience first.
Additional content considerations
Don’t just chase keywords – make sure your content delivers value. Use keyword research to understand search intent and create content accordingly. Pay attention to content format as well – some topics may be better suited for videos, guides, listicles, etc.
Use tools like word counters and readability analyzers to optimize length and readability. Visuals and multimedia can also help make content more engaging.
On-Page Optimization and Tracking
Optimizing page elements
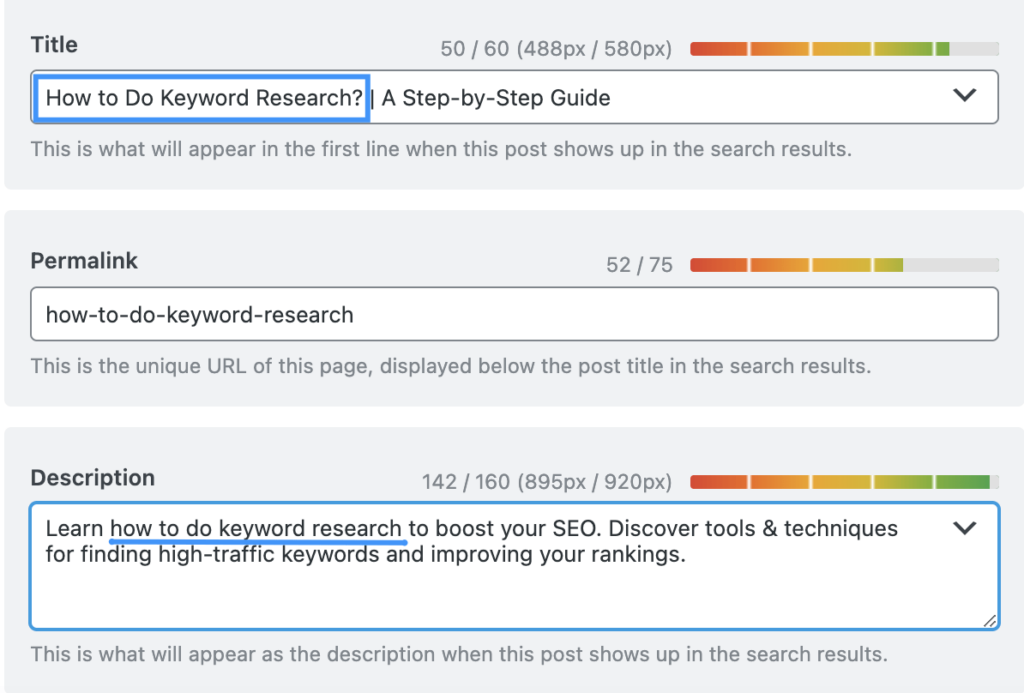
In addition to the content itself, optimize all on-page elements like title tags, meta descriptions, headers, and URL structures using your target keywords. This helps search engines understand what each page is about and should rank for.
Monitoring and refining performance
After publishing, continuously track your pages’ rankings, search traffic, and engagement metrics for your targeted keywords. If performance is lacking, further refine and optimize the content. An ongoing cycle of publishing, tracking, analyzing, and adjusting based on results is crucial.
Use rank-tracking software to monitor keyword rankings across multiple search engines over time. In Google Analytics, set up filtered views to specifically track your focus keywords.
Review engagement metrics like average session duration, pages per session, and bounce rates – low numbers may indicate content needs improvement. Stay patient and allow time to accrue data before making rash changes.
Common Keyword Research Mistakes to Avoid
Overusing Keywords
One critical mistake to avoid in keyword research is overusing or “stuffing” keywords onto your pages. Repeatedly using the same exact keyword unnaturally is considered keyword stuffing, and it damages the user experience.
Not only does it make your content hard to read, but keyword stuffing is also considered a black hat SEO tactic. Search engines can actually penalize sites that overdo it with excessive keyword repetition. Use target keywords naturally and moderately across titles, headers, body copy, etc.
Ignoring Search Intent
Another big mistake is ignoring the search intent behind the keywords you want to target. Before optimizing any content, you need to understand the driving intent and motivations of the user performing that search query. Are they looking for information? Trying to navigate somewhere specific? Or are they ready to make a purchase?
Your content needs to satisfy that intent completely. Create different content optimized around different keyword sets for each of the major search intent types – informational, navigational, and commercial/transactional intents.
Focusing Only on High-Volume Keywords
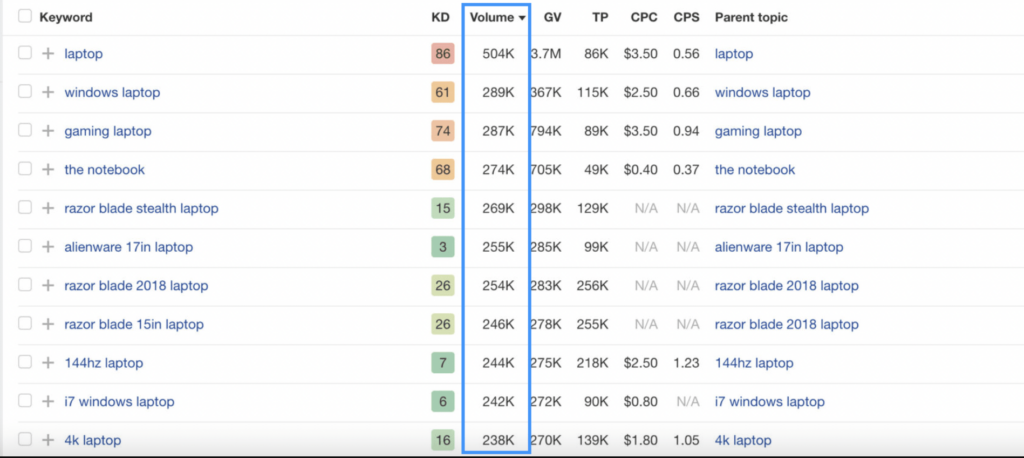
Many businesses also make the mistake of only chasing after high-volume, broad keyword terms while ignoring other valuable opportunities. Long-tail keywords, which are longer, more specific keyword phrases, can actually drive very targeted, relevant traffic. Because long-tails have less competition due to lower search volumes, they are often easier to rank for.
Don’t neglect opportunities in your keyword research just because a term has a relatively lower search volume.
Look at engagement metrics – long-tails often have higher click-through rates from motivated searchers. Cover niche topics and subtopics thoroughly by targeting clusters of related long-tails. Over time, the cumulative traffic from many well-ranking long-tails can supersede that of a single broad keyword.
Conclusion
Effective keyword research is the cornerstone of any successful SEO and digital marketing strategy. By following the best practices outlined in this guide, you can learn how to do keyword research effectively. This approach helps uncover relevant, high-value keywords that drive targeted traffic and conversions.
Remember to prioritize user intent, diversify with long-tail keywords, and optimize content holistically. Avoid common pitfalls like keyword stuffing and neglecting search intent. Continuously monitor performance, adjust your approach, and stay up-to-date with the latest trends and algorithm updates.